Installing a Rainwater Collection System: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction to Rainwater Collection Systems
Rainwater collection systems have become an increasingly popular solution for homeowners and businesses looking to conserve water, save on utility bills, and reduce their environmental footprint. By capturing and storing rainwater, these systems provide an alternative water source that can be used for various purposes, such as irrigation, flushing toilets, and even potable water when properly treated. With growing concerns over water scarcity and environmental sustainability, installing a rainwater collection system is not only a practical choice but also an environmentally responsible one.
Implementing a rainwater collection system involves understanding the components, installation process, and maintenance requirements. This guide will walk you through the essential aspects of setting up a system that meets your needs and complies with local regulations.
Components of a Rainwater Collection System
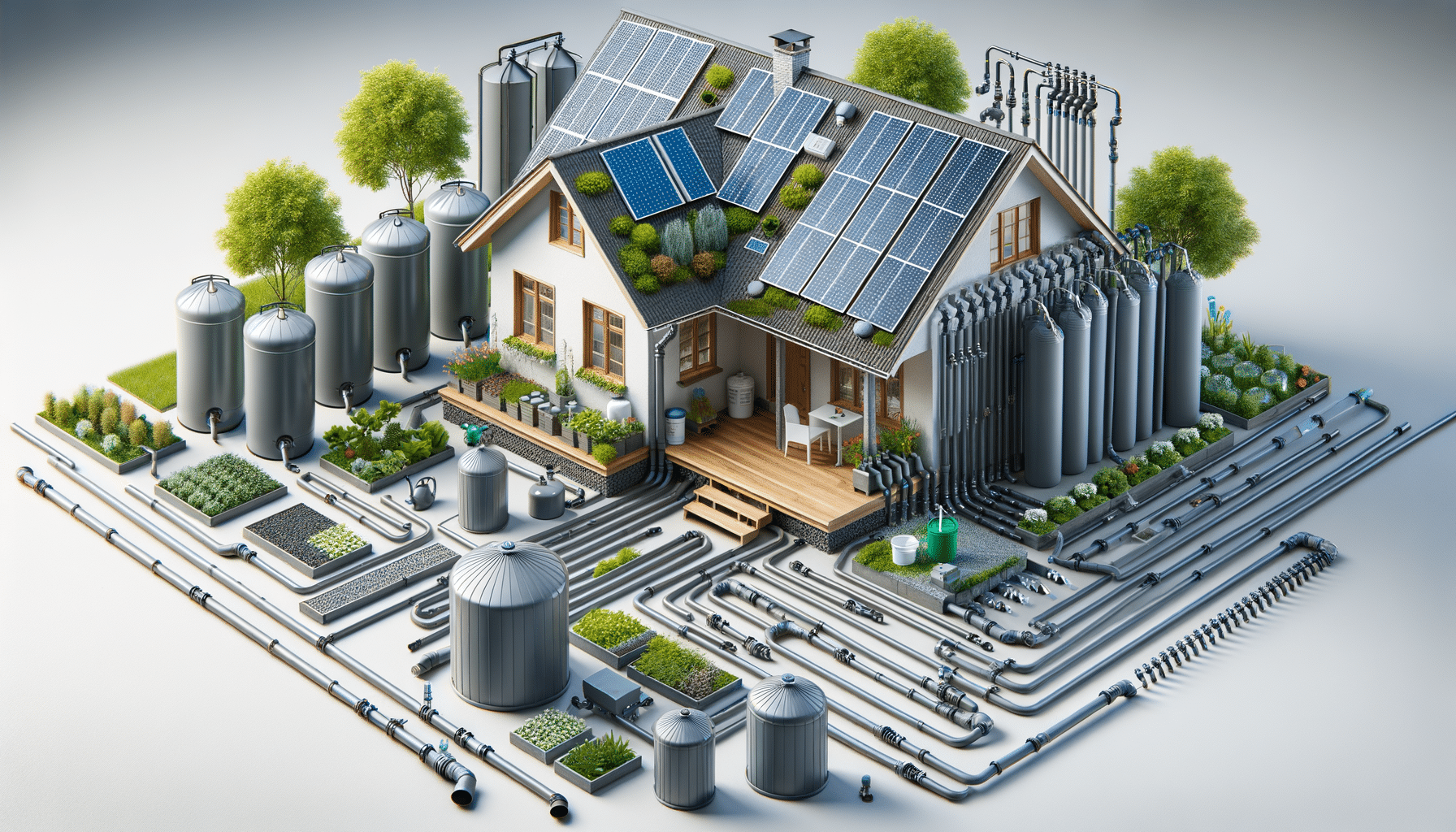
A rainwater collection system consists of several key components that work together to efficiently capture and store rainwater. Understanding these components is crucial for designing a system that suits your specific requirements.
- Catchment Area: Typically, the roof of a building serves as the catchment area, where rainwater is collected. The type and condition of roofing material can affect the quality of collected water.
- Gutters and Downspouts: These direct rainwater from the roof to the storage system. It’s important to ensure gutters are clean and properly sloped to facilitate water flow.
- First Flush Diverter: This device prevents the initial runoff, which may contain debris and contaminants, from entering the storage tank.
- Storage Tanks: Tanks come in various sizes and materials, such as plastic, concrete, or metal. The choice depends on the volume of water you wish to store and the available space.
- Filtration and Treatment System: To ensure water quality, especially if it’s intended for potable use, filtration and treatment systems are essential.
Each component plays a vital role in the effectiveness and efficiency of the rainwater collection system. Proper selection and installation are key to maximizing benefits.
Installation Process
The installation of a rainwater collection system requires careful planning and execution. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
1. Assess Your Needs: Determine the purpose of the collected rainwater. Will it be used for irrigation, household use, or drinking? This will influence the design and components of your system.
2. Design the System: Based on your needs, design a system that includes all necessary components. Consider factors such as roof size, rainfall patterns, and available space for storage tanks.
3. Obtain Permits: Check local regulations and obtain any necessary permits. Some areas have restrictions on rainwater harvesting, so it’s important to ensure compliance.
4. Install Gutters and Downspouts: Ensure they are properly sloped and free of debris to efficiently channel water to the storage tank.
5. Set Up the Storage System: Install the storage tanks in a suitable location, ensuring they are stable and secure. Connect the tanks to the downspouts and include a first flush diverter.
6. Install Filtration and Treatment: If the water is for potable use, ensure proper filtration and treatment systems are in place to meet health standards.
Following these steps will help ensure a successful installation, allowing you to effectively harvest rainwater for your intended use.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the longevity and efficiency of your rainwater collection system. Here are some maintenance tips and troubleshooting advice:
- Clean Gutters and Downspouts: Regularly remove debris to prevent blockages that can impede water flow.
- Inspect Storage Tanks: Check for leaks or cracks that could lead to water loss or contamination.
- Monitor Water Quality: Test the water periodically, especially if it’s used for drinking, and adjust filtration and treatment as needed.
- Check for Algae Growth: Ensure tanks are opaque or covered to prevent sunlight exposure, which can promote algae growth.
If you encounter issues with your system, such as reduced water flow or poor water quality, troubleshooting may involve checking for blockages, ensuring all components are properly connected, and verifying that filtration systems are functioning correctly.
By staying proactive with maintenance, you can ensure your rainwater collection system operates smoothly and efficiently.
Benefits of Rainwater Collection Systems
Installing a rainwater collection system offers numerous benefits, both for individual users and the environment. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Water Conservation: By capturing rainwater, you reduce reliance on municipal water supplies, conserving a precious resource.
- Cost Savings: Lower water bills can result from using collected rainwater for irrigation or household needs.
- Environmental Impact: Reducing runoff helps decrease soil erosion and pollution in local waterways.
- Self-Sufficiency: Having an independent water source can be invaluable during droughts or water restrictions.
These benefits make rainwater collection systems an attractive option for those seeking sustainable and cost-effective water management solutions.